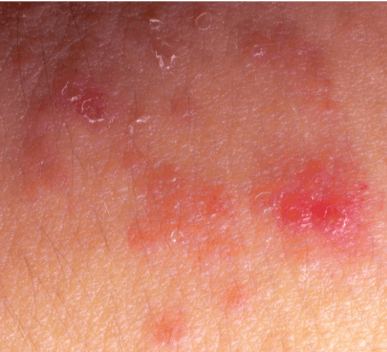
Eczema is the broad term for a group of medical conditions in which patches of skin become red, inflamed and rough. There are several types of eczematous skin conditions including atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, and nummular dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema. The term atopic applies to a group of diseases, often hereditary, that can lead to other allergic conditions, including hay fever and asthma.
Eczma is not contagious. You cannot “catch” this condition from another person.