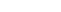Hives are skin lesions caused by allergens that trigger a defense reaction in your body. The rash appears as raised, typically oval-shaped welts that can form anywhere on the body. Hives is the common name for the condition known as urticaria.
Tues: 8:30am - 3:00pm
Wed: 12:00pm - 6:00pm
Thurs: 8:30am - 3:00pm
Fri: Closed
Sat: 8:30am - 12:30pm
Sun: Closed
Greenvale, NY 11548
Hives

What is hives?
What causes hives?
Hives are triggered by your body’s allergic reaction to specific foods and substances. Allergens causing hives will vary from person to person. When you encounter an allergen, your body produces histamine and other chemicals below the surface of your skin. The histamine and chemicals release fluids that accumulate under your skin, resulting in a breakout of hives.
In about half of all hives cases the exact cause is never determined. However, known triggers in many people include foods such as shellfish, eggs, nuts, wheat and strawberries. Other known triggers are insect bites, pet dandruff, some types of medicines (including aspirin and antibiotics), bacterial infections, dust mites, intestinal parasites, contact with certain chemicals, pollen and products made of latex. These are some of the most common triggers, but there are many more exposures that can cause this reaction. Not all allergens affect all people.
How dermatologists diagnose hives
Your dermatologist will examine your skin where the hives form and ask questions to try to identify what allergen triggered the outbreak. You’ll want to discuss any medications, herbal remedies or supplements you take, what you eat and drink, where your hives appear and how long they last, and where the welts are painful.
Your dermatologist may recommend blood tests or skin tests to determine what causes your hives.
How dermatologists treat hives
In mild to moderate cases, your dermatologist may recommend over-the-counter antihistamines to reduce the swelling and itching of hives. For treating chronic hives or hives that do not respond to over-the-counter medications, your dermatologist may recommend prescription-strength antihistamines. These medicines may cause drowsiness.
Your dermatologist may also advise you take a combination of medicines to treat hives. Some of these medicines include histamine (H-2) blockers which are injected or taken orally, anti-inflammation medications such as prednisone to reduce swelling and itching, or immune-suppressing drugs and injections which are reserved for severe cases.
Chronic hives can recur for months and even years without effective treatment. The intense itching from hives can interfere with work and sleep, and in some cases cause difficulty breathing, so it’s important to discuss your condition with your dermatologist before hives impact your quality of life.
If you are concerned about hives, click here to schedule an appointment with our board-certified dermatologists or walk into Walk-in Dermatology at your convenience for immediate evaluation.