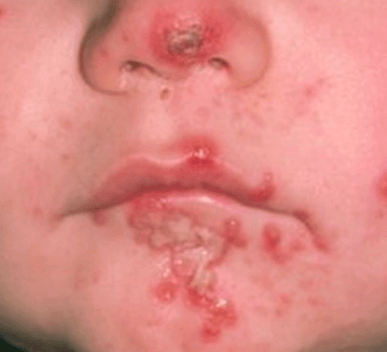
Impetigo is a bacterial skin infection characterized by sores which can spread quickly. Anyone can develop impetigo, although it is most common in babies and young children.
The skin sores can appear anywhere on the body, but children tend to get them on their face and sometimes on their arms or legs.
Children with impetigo may be unable to resist scratching the affected area, causing the infection to spread across the surrounding skin and other areas of the body the child might touch. Untreated sores may cause scarring and skin discoloration.