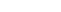Vitiligo is a skin condition that is characterized by patches of depigmented skin. Vitiligo affects millions of people worldwide and is seen equally in men and women and across all skin types. The depigmented patches can occur on any area of your body, including hair, eyelids, and genitalia. Once a patch of vitiligo develops it is difficult to predict whether it will spread, how much it will spread, or if new patches will develop.
Tues: 8:30am - 3:00pm
Wed: 12:00pm - 6:00pm
Thurs: 8:30am - 3:00pm
Fri: Closed
Sat: 8:30am - 12:30pm
Sun: Closed
Greenvale, NY 11548
Vitiligo

What is vitiligo?
What causes vitiligo?
Vitiligo occurs when cells in the body stop producing the dark brown to black pigment called melanin, which is produced by melanocytes and causes skin to darken when exposed to sunlight. There are different subtypes of vitiligo depending on presentation and extent of pigment loss, some of which may be hereditary and others which can be caused by sunburn or exposure to toxic chemicals.
How dermatologists diagnose vitiligo
Your dermatologist will take a thorough medical history and closely examine your skin for signs of vitiligo, which present as patches of depigmented skin. The discoloration typically appears first on areas of the body regularly exposed to sunlight, including your face, lips, hands, arms and feet.
Other signs of vitiligo may include premature hair whitening or graying on your head, eyelashes, eyebrows or beard; loss of color in the retina of the eye and loss of color in the mucous membrane lining of your mouth and nose.
Family history of vitiligo may also help in the diagnosis as the condition can be genetic. Personal history of autoimmune disease is also important to determine as vitiligo can be seen with other conditions such as a thyroid disorder.
There are several skin conditions that can look similar to vitiligo including pityriasis alba and tinea versicolor, so a thorough work up and evaluation is necessary for diagnosis.
How dermatologists treat vitiligo
Vitiligo is neither contagious nor life-threatening. However, the resulting dyspigmented skin may be associated with decreased self-esteem and psychological stressors. While there is no known cure for vitiligo, your dermatologist can develop an individualized treatment plan to minimize the spread of the condition and help restore pigmentation to the affected areas of the body.
Anti-inflammatory corticosteroid creams are most effective in treating newer, active areas by minimizing the spread of the pigmentary changes and restoring some pigmentation in depigmented areas. Nonsteroidal topical anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed for long term maintenance of the condition.
Exposing the affected areas of skin to ultraviolet light can sometimes stimulate pigment growth. Although this can be an effective treatment, especially in the areas of the face and neck, you may need ultraviolet light therapy two to three times a week for months to years for best results. Talk to your dermatologist if you are considering this treatment option as prolonged exposure to UV light can increase your risk of developing skin cancer.
In some cases, your dermatologist may propose treatment with an excimer laser to help restore pigmentation. This device delivers targeted light therapy more precisely to specific areas of involvement.
Depending on the extent and severity of your condition, you and your dermatologist may determine that surgery is the right choice of treatment for you. There are three main types of surgeries for treating vitiligo: skin graft, blister graft, and tattooing, which attempts to match skin tones by coloring the area affected by vitiligo. Each of these procedures carries a risk of scarring and potentially triggering vitiligo on other areas of the body.
Sun protection is especially important if you have a diagnosis of vitiligo. The depigmented areas lack the melanin cells that protect us from UV damage and sunburn. Broad spectrum, water-resistant sun protection, preferably with a mineral based sunscreen containing zinc or titanium dioxide and SPF 30 or higher, should be used regularly along with general reduction of exposure to the sun’s rays.
If you are concerned about vitiligo, click here to schedule an appointment with our board-certified dermatologists or walk into Walk-in Dermatology at your convenience for your evaluation.