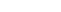Tues: 8:30am - 3:00pm
Wed: 12:00pm - 6:00pm
Thurs: 8:30am - 3:00pm
Fri: Closed
Sat: 8:30am - 12:30pm
Sun: Closed
Greenvale, NY 11548
What Happens if you Accidentally Scratch Off a Mole?

A mole is a small cluster of pigmented cells that appears on your skin. Common moles or nevi can appear anywhere on your body, but are usually located in areas affected by sun exposure. Most adults have between 10 and 40 moles on their skin, and new moles continue to develop as a person ages. Much like any other part of your body, moles can be injured by tearing or scratching.
So what will happen if you unintentionally scratch off a mole? Scratching off a mole will probably cause some bleeding, but should not require medical treatment. However, if a mole continues to bleed, it should be examined by a dermatologist. Note however, that a growth on the skin that continually bleeds may be a warning sign of skin cancer.
What if your Mole Gets Scratched?
When a raised mole is scratched or pulled on, it will most likely bleed. Other triggers that can cause a mole to bleed include catching it on clothing or jewelry, applying make-up or skin care products near it, rubbing an insect bite, or removing hairs around it.
This occurs because the surrounding skin underneath the mole was injured, which makes it appear like your mole is bleeding. The skin vessels underneath the mole may also weaken and become prone to injury. If the mole itches, you might break the skin surrounding it by scratching too hard.
While a bleeding mole may be painful, it can be treated easily at home. You don’t need to be too concerned about moles that are bleeding or oozing fluids due to injury. However, you should visit a dermatologist if it seems to be bleeding for no reason. Bleeding moles that resemble open sores may be a sign of melanoma, which is a form of skin cancer.
How Bleeding Moles are Treated
If you injured yourself and have a bleeding mole, here are some basic first aid steps:
- Apply a cotton ball with rubbing alcohol to sterilize the wound
- Put some pressure on the area to stop the bleeding
- Cover the area with a bandage, but avoid getting adhesive on the surrounding skin
- Call your dermatologist if the mole continues to bleed
The last step is necessary because even though most common mole injuries do not require further treatment, a continually bleeding mole may indicate skin cancer. If that is the case, your doctor may recommend you undergo a biopsy. This involves taking a skin sample to check for the presence of cancer cells.
In order to conduct a biopsy, your dermatologist will recommend removing the suspicious growth through an outpatient procedure. It may be done using a surgical excision or a shave excision.
- Surgical excision: For a surgical excision, the dermatologist will numb the area, cut off the mole with a scalpel, and stitch up the wound.
- Shave excision: Your dermatologist will numb the area and shave off the raised mole with a sharp blade. A shave excision is usually done on smaller moles.
Once a mole is removed, it usually does not come back. If your mole does grow back, it’s important to consult with your doctor immediately.
Three Reasons Not to Remove a Mole at Home
Although some moles may be itchy or pesky, patients are warned against trying to remove moles on their own. Here’s why:
- Shaving or cutting your mole can disfigure your skin and leave a scar if done improperly
- Removing a mole without sterile equipment in a nonsurgical condition may lead to infection
- If your mole is cancerous, the cells can remain in the skin and spread
Can a Scratched Mole Cause Cancer?
Scratching a mole does not cause skin cancer to develop. Scratching can cause bleeding and infection, microscopic injuries, or an outright wound. There are no documented cases where a person scratching a mole later developed cancer as a result.
It’s a common misconception that all skin cancers begin as moles. There are different forms of skin cancer, the rarest and most deadly being melanoma. Cancerous moles contain melanocytes, which have a mutation in a cancer-related gene that can cause them to grow and multiply. However, a vast majority of these melanocytes do not turn cancerous and just “sleep.” In fact, only 20-30% of melanomas occur in pre-existing moles.
Identifying Cancerous Moles
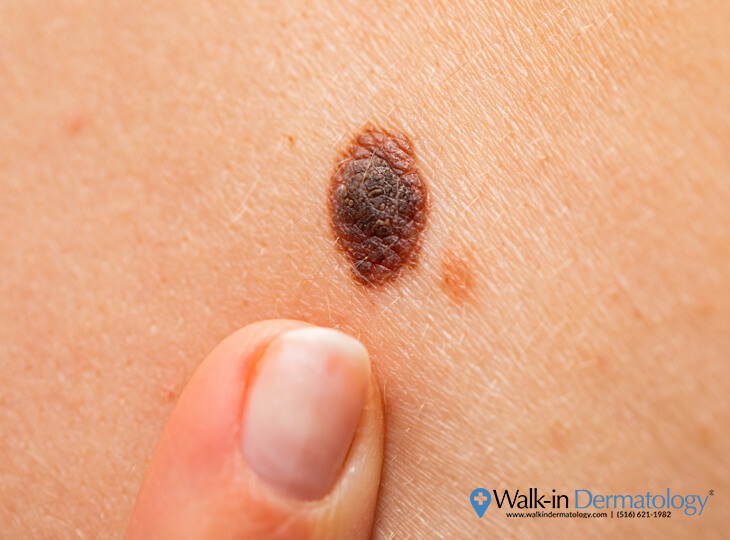
If your mole is bleeding for no apparent reason, it’s important to have it checked since the bleeding may be caused by skin cancer. Other symptoms of a cancerous growth follow the “ABCDEs:”
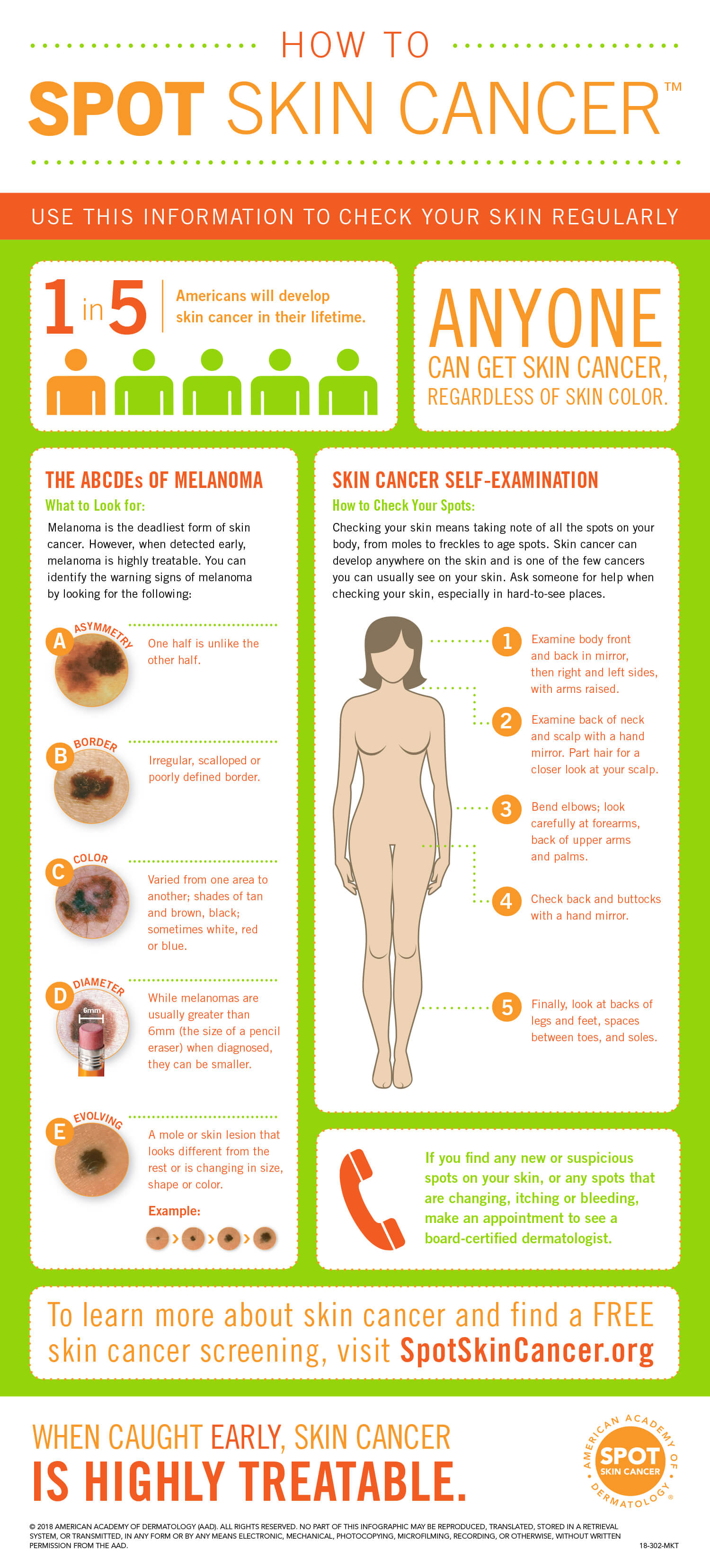

- Asymmetry: A mole is considered asymmetrical if it has an odd shape or its two halves do not match.
- Border: One possible warning sign of cancer is if the border of the spot is ragged. The border of cancer-free growths will have smooth and even borders.
- Color: A multi-colored or unevenly colored growth may indicate cancer, while non-cancerous growths will remain a single shade of brown.
- Diameter: A benign mark usually has a small diameter, while cancerous moles are typically larger than a pea or a pencil eraser.
- Evolving: A cancerous growth may change in size, shape, color, or elevation over time.
An early diagnosis is the best way to manage this potentially-life threatening disease. Having a full body scan done by a board-certified dermatologist can help detect, remove, and cure cancerous areas.
Let Walk-in Dermatology Treat Your Moles
If you’re conscious about the appearance of your moles or concerned about growths on your skin, Walk-in Dermatology can help. Our team of board-certified dermatologists and experienced medical staff will address your concerns and provide necessary treatment for all your skin conditions. You can also schedule an appointment with us for mole removal. Don’t wait, contact us today.